Github地址:
https://github.com/xiandanin/LoadingBar
前言
Loading是很普遍的需求,比如请求的时候需要显示Loading,请求完成以后再取消Loading,而一般的实现方式是在布局xml里添加一个ProgressBar,但是这样写就有很多不便,每个页面的layout都要写一个ProgressBar,显示的位置也固定了,还耦合了很多代码。
而LoadingBar就是为了跟方便的操作Loading而生,高度解耦,样式全部通过工厂类决定。
结构介绍
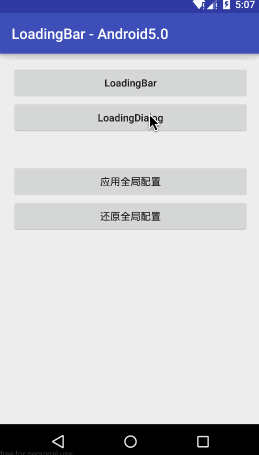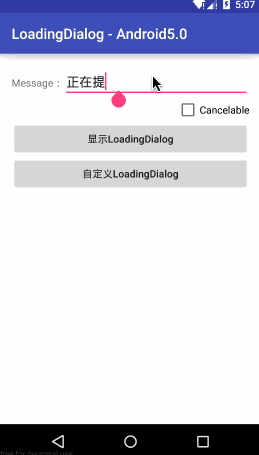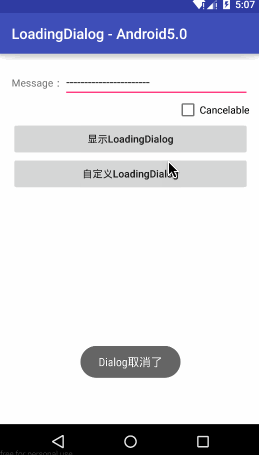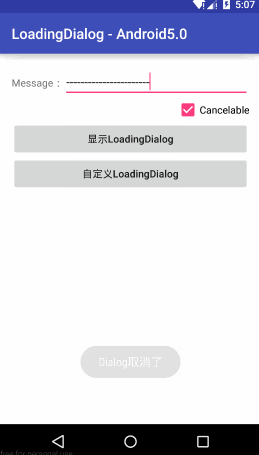
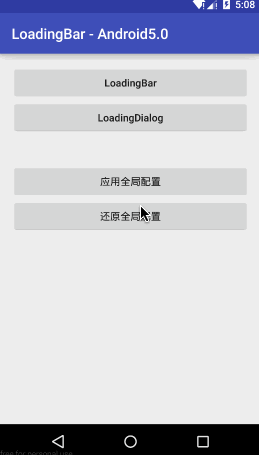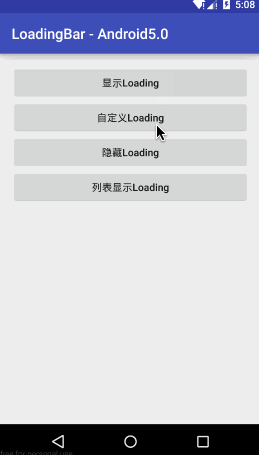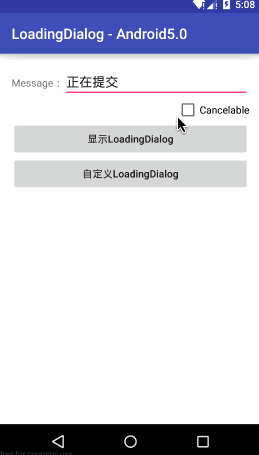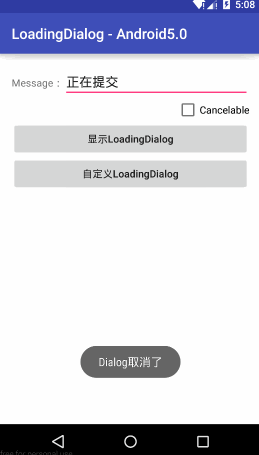
LoadingBar - 适合一些显示数据的操作,比如请求列表
LoadingDialog - 适合一些提交数据的操作,比如注册,登录
Factory - 决定了loading的样式,自定义样式只需实现Factory
快速开始
Android Studio - 在build.gradle中引入
1 | compile 'com.dyhdyh.loadingbar:loadingbar:1.4.7' |
LoadingBar
1 | //默认样式 loading将会覆盖在parent的内容上面 |
LoadingDialog
1 | //默认样式 |
自定义Factory
1 | public class CustomLoadingFactory implements LoadingFactory { |
全局配置
1 | //自定义样式并应用于全局 |
资源释放
其实LoadingBar在cancel的时候已经释放掉了,可以不用手动释放,但是这里也提供释放的方法,根据自己需要选择
在Activity onDestroy调用,个人建议在BaseActivity,资源释放只会释放无效的资源1
LoadingBar.release();
源码解析
定义结构
首先我一开始就想好了,这得有三样东西,LoadingBar与LoadingDialog,用Factory来生产loading所需要的View和Dialog
定义接口
两者的共同点是都会有显示,所以我定义了一个共用的接口1
2
3public interface ILoading {
void show();
}
LoadingBar除了有show还得有cancel1
2
3public interface ILoadingBar extends ILoading {
void cancel();
}
LoadingDialog最终都是操作Dialog,所以它得有create,再附加一些设置常用属性的方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public interface ILoadingDialog extends ILoading {
Dialog create();
ILoadingDialog setCancelable(boolean flag);
ILoadingDialog setMessage(CharSequence message);
}
LoadingFactory onCreateView返回的View就决定了Loading长什么样1
2
3
4public interface LoadingFactory {
View onCreateView(ViewGroup parent);
}
DialogFactory 主要是onCreateDialog,这个方法决定了Dialog长什么样,在这里实现创建Dialog1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public interface DialogFactory {
/**
* 创建dialog
* @param context
* @return
*/
Dialog onCreateDialog(Context context);
/**
* 设置提示消息
* @param dialog
* @param message
*/
void setMessage(Dialog dialog,CharSequence message);
/**
* 进入退出的动画id
* @return
*/
@StyleRes int getAnimateStyleId();
}
LoadingBar的实现
其实就是需要两个View,mView就是factory.onCreateView返回的LoadingView,mParent就是现实1
2
3
4private LoadingBar(ViewGroup parent, LoadingFactory factory) {
mParent = parent;
mView = factory.onCreateView(mParent);
}
然后把mView添加到mParent里,这样mView就处于最上层,覆盖着内容,这样就达到了Loading的效果1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public void show() {
if (mView != null) {
mView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
if (mView.getParent() != null) {
mParent.removeView(mView);
}
mParent.addView(mView);
}
}
取消很简单,就直接把mView移除掉就好了1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public void cancel() {
if (mView != null) {
mView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mParent.removeView(mView);
mView = null;
if (this.mListener != null) {
this.mListener.onCancel(mParent);
}
}
}
值得一说的还有findSuitableParent,因为Loading是要在可覆盖的布局上才有作用的,而当parent传的是非覆盖的布局(例如LinearLayout),这个方法会一直往外层寻找可覆盖的布局1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private static ViewGroup findSuitableParent(View parent) {
if (parent == null) {
return null;
}
View suitableParent = parent;
do {
if (suitableParent instanceof FrameLayout || suitableParent instanceof RelativeLayout ||
"android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout".equals(suitableParent.getClass().getName()) ||
"android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout".equals(suitableParent.getClass().getName()) ||
"android.support.v7.widget.CardView".equals(suitableParent.getClass().getName())) {
return (ViewGroup) suitableParent;
} else {
final ViewParent viewParent = suitableParent.getParent();
suitableParent = viewParent instanceof View ? (View) viewParent : null;
return (ViewGroup) suitableParent;
}
} while (suitableParent != null);
}
LoadingDialog的实现
构造方法先用factory创建了dialog,如果有动画设置动画1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public LoadingDialog(Context context, DialogFactory factory) {
this.mDialog = factory.onCreateDialog(context);
this.mFactory = factory;
int animateStyleId = this.mFactory.getAnimateStyleId();
if (animateStyleId > 0) {
this.mDialog.getWindow().setWindowAnimations(animateStyleId);
}
}
因为Dialog是单例,如果在Activity已经finish了再去操作做个Dialog的话,就会抛异常,所以在show与cancel的时候要先检查是否能够操作1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public void show() {
if (isValid() && !mDialog.isShowing()) {
mDialog.show();
}
}
public void cancelDialog() {
if (isValid() && mDialog.isShowing()) {
mDialog.cancel();
}
}
private boolean isValid() {
if (mDialog != null) {
Context context = mDialog.getContext();
if (context instanceof ContextWrapper){
context = ((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext();
}
if (context instanceof Activity) {
if (!((Activity) context).isFinishing()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
总结
使用场景不局限于请求,其实还有很多异步操作都能用上
比如压缩图片,也可以用LoadingDialog
更多玩法等你挖掘,有问题可以去Github的issue提出